Requests
约 1658 个字 350 行代码 3 张图片 预计阅读时间 10 分钟
HTTP for Humans™
官方项目的第三方模块
安装
用 pip 安装(注意拼写,后面有 s):
构建简单的 HTTP 请求
一个简单的 GET 请求
与 urllib 对比
urllib 需要先构建请求,再获取响应;Requests 在构建请求时即可获取响应。
urllib 需要、得到的数据类型是特有的,需要用特有的方法去构建、解析;Requests 需要、得到的数据类型通常是基本的,绝大多数不需要特别构建、解析。
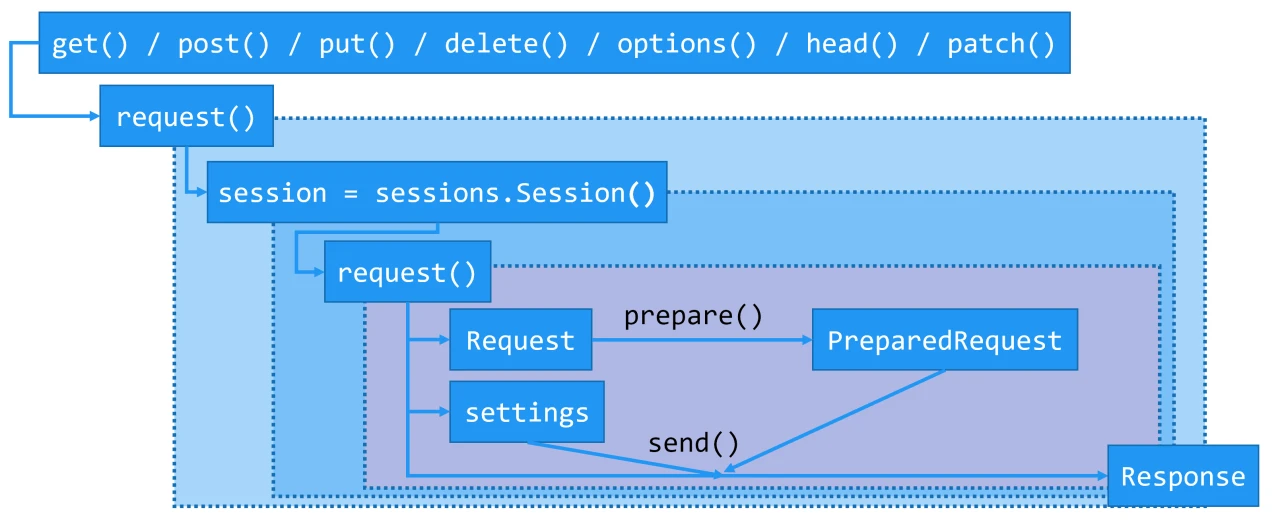
基本原理
底层基于第三方模块 urllib3;下面省略模块、对象名
构建请求所用的方法语句
这些方法的实质为 requests.request(HTTP方法的小写字符串, URL[, ...]),最终返回 requests.Response 对象。
常用参数如下:
| 参数名 | 数据类型 | 含义 |
|---|---|---|
params |
字典 /元组列表 / bytes |
发送到 URL 的参数 |
data |
字典 / 元组列表 / bytes / 文件对象 |
发送到请求主体的参数 |
headers |
字典 | 定义首部行 |
json |
字典 | 发送到请求主体的 JSON(可代替 data) |
files |
包含文件对象的字典 | 发送到请求主体的文件 |
cookies |
字典或 CookieJar 对象 |
和请求一并发送的 Cookie |
auth |
元组 | 需要验证身份时填的信息 |
timeout |
浮点数或元组 | 超时时间 |
allow_redirects |
布尔值 | 是否允许重定向(默认为是) |
proxies |
字典 | 代理设置 |
verify |
布尔值或字符串 | 是否验证 TLS 证书(默认为是),或指定 CA 证书路径 |
stream |
布尔值 | 若为否,立即下载响应内容 |
cert |
字符串或元组 | SSL 客户端密钥(pem),或表示 (证书名, 密钥) 的元组 |
构建带参数的请求
参数分 params(放在请求 URL)和 data(放在请求实体)。
data 可以为字典、元组列表、bytes、文件对象、字符串等类型。
会自动进行 URL 编码,自动添加需要的首部。
构建请求主体为 JSON 的请求
请求主体为 JSON 字符串时,建议使用 json 参数,而非 data。前者可以自动把请求首部的 Content-type 填为 application/json。
发送文件
files 里面最常见的结构如下:
文件要在二进制模式下打开。
如果混有文件和数据,分别写到 files 和 data 中,Requests 会自动帮忙处理好。
猜测文件的 MIME 类型
如果你事先不知道文件的 MIME 类型,可以使用标准库 mimetypes 猜测:
例
Response 对象的属性和方法
查看 Response 对象的属性和方法,显示所有可用的属性和方法(不包含以下划线开头的):
-
status_code:整数,HTTP 状态代码: -
ok:布尔值,HTTP 状态代码是否小于 400该属性还用于整个对象的布尔值(
__bool__()): -
raise_for_status():如果想要在请求发生 4XX 或 5XX 错误时抛出异常,可以使用它:如果有错误,抛出
requests.exceptions.HTTPError;否则,返回
None: -
reason:字符串,HTTP 状态的文本: -
url:字符串,最终请求的 URL。如请求时有params参数,也会同时把参数写进去: -
headers:字典,响应首部行。键为字段名,值为字段值 -
cookies:返回 Cookies,数据类型为requests.cookies.RequestCookieJar,里面是 Cookie 信息。可以像字典一样操作;也可以转为字典:
-
encoding:字符串,响应的编码。默认情况下通过响应首部行的charset字段得出,但是可以更改该属性的值,以强制定义编码: -
apparent_encoding:同上,但是使用chardet模块,通过内容猜测得出: -
links:字典,返回响应首部的 Link 字段的信息;如无,返回空字典Link 字段的格式如下:
-
elapsed:表示响应时间,数据类型为datetime.timedelta。这里的响应时间,指的是从“发送请求的第一个字节”开始,到“解析完响应的首部行”为止,与响应主体的大小无关。
-
content:字节对象,响应主体(如果想下载文件,取这个) -
text:同上,但数据类型是字符串 -
json(**kwargs):如响应主体是 JSON 格式的文本,可以用该方法转为字典或列表这样的 Python 可以直接处理的格式- 该方法使用
complexjson模块,兼容json.loads()的附加参数 - 如出错,抛出
requests.exceptions.RequestsJSONDecodeError异常
- 该方法使用
-
history:列表,表示重定向的历史- 如果请求被重定向,该属性记录了重定向的历史:里面每一个元素都是 Response 对象,表示重定向到的请求;重定向多少次,里面就有多少请求
- 如果没有被重定向,该属性为空列表
-
is_redirect:布尔值,该请求是否被重定向(HTTP 状态码是否为301、302、303、307或308)重定向的请求的最后一步为
False,之前的步骤(history里面的)的为True。接上例 -
is_permanent_redirect:布尔值,该请求是否被永久重定向(HTTP 状态码是否为301或308)接上例 -
iter_content()和iter_lines():都是返回一个生成器,可迭代,迭代结果的类型都是字节类型- 前者依次迭代响应主体的一个字节
- 后者依次迭代响应主体的一行
-
request:返回requests.models.PreparedRequest类,其中包含许多于请求相关的属性,如:url:URL(如果有参数,也会写在里面)body:请求实体,为bytes对象- 将请求实体的内容转为文本:
r.request.body.decode(errors='ignore')
- 将请求实体的内容转为文本:
headers:请求首部
close():关闭请求- 执行完之后,最好关闭它
- 关闭后仍然可以访问大部分内容
- 也可以像打开文件一样,利用
with语句构建请求
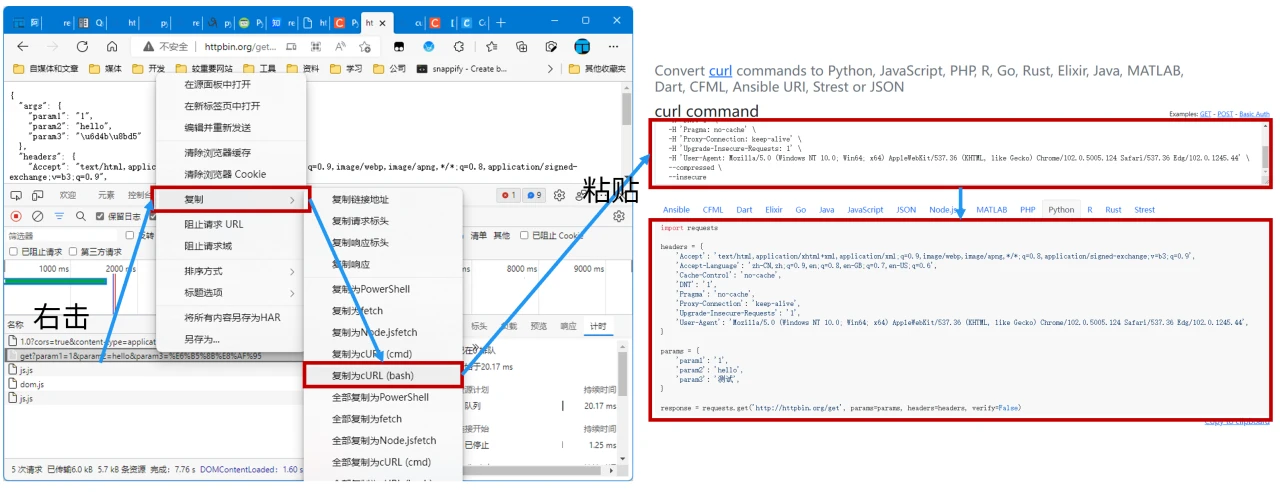
快速转换 cURL 命令行到 Python 的 Requests 代码
https://curlconverter.com/#python
Cookie 的传递
默认情况下 Cookie 不会叠加
先发送第一个请求:
此时的 Cookie:
再发送另一个请求:
该请求的 Cookie:
可以发现之前的 Cookie 未随之而来;因为 r2.cookies 只记录了这个请求传回的 Cookie,未进行叠加。
但实际上,浏览器里面此前的 Cookie 是会保留的,下次请求会一并发送出去。
手动叠加
RequestsCookieJar 对象没法直接叠加,但可以转为字典之后叠加,字典可以作为 Cookie 传入请求:
利用 Session 对象
requests.sessions.Session 对象可以创建一个会话,会话中建立的请求会共享一些信息,如 Cookie。
为了简化代码,可以定义这个会话的首部字段:
发送第一个请求:
之后不需要动 Cookie,会自动发送;为了更好地模拟,可以把首部的 referer 字段改一下:
此时的 Cookie:
Session 对象也可以像 Response 对象一样,使用 close() 关闭。